Overview
Rather than simply focusing on a mark from piece of assessment, students need to be encouraged to proactive recipients of feedback, not only to improve on future assessment outcomes but also to develop relevant transferrable skills. Feed-forward is therefore an essential component of feedback.
Key Principles
When seeking to enhance student learning through feedback the following principles apply:
Good Practice
- Peer Discussions - Provide time in teaching and tutorial sessions for students for student to discuss feedback comments with their peers in class and develop a range of strategies for development.
- Reflective Portfolios - Encourage students to keep a record of their assessment feedback throughout their programme and make reflections on this. Use tutorials to discuss these.
- Individual learning plans - Use feedback to support students in developing individual learning plans. Use tutorials to discuss these.
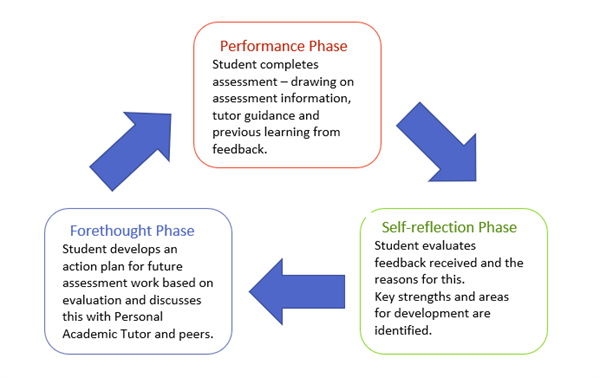
Zimmermann's (2002) Phases of Self-Reflection - Applied to Student Learning from Assessment and Feedback
Further Reading
Advance HE (2016) The Developing Engagement with Feedback Toolkit (DEFT) [online] Available from: https://www.advance-he.ac.uk/knowledge-hub/developing-engagement-feedback-toolkit-deft
Advance HE (2020) On Your Marks: Learner-focused Feedback Practices and Feedback Literacy [online] Available from: https://www.advance-he.ac.uk/knowledge-hub/your-marks-learner-focused-feedback-practices-and-feedback-literacy
Carless, D & Boud, D. (2018) The Development of Student Feedback Literacy: Enabling Uptake of Feedback. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, pp.1315–1325.
Duncan, N. (2007) Feed-forward: Improving Students' Use of Tutors' Comments. Assessment & Evaluation in HIgher Education 32(3), pp.271-283.
Holmes, K and Papageorgiou, G (2009) Good, bad and insufficient: Students’ expectations, perceptions and uses of feedback - http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.456.5943&rep=rep1&type=pdf